Participants Of Stock Market And Settlement Process

1. Investors/Traders:
Any person investing in the stock market with an expectation of future financial return is called an Investor. The main objective of an Investor is to maximize their wealth or gain return instead of speculation. These investors invest in the securities with a view to hold them in the long run. These investors prefer Buy and Hold strategy.
Traders are the people who trade their shares or securities for a consideration with others in the market with a view to earn profits. These traders invest in the securities for a short term. Their main objective is earning profits when the price increases instead of wealth maximization.
2. Stock brokers:
A person licensed by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to trade at the Stock Exchange is called a Stock broker. These people act as agents or intermediaries between the traders or investors. These Stock brokers charge commission on the transactions.
There are currently 133 stock brokerage houses.
There are currently 2 types of stock brokers based on the way of trading they do,
- Traditional or Conventional Stock brokers: Stockbrokers who do trading after obtaining consent from the buyers or sellers either through written or tele communication.
- Online Stock brokers: These are the stock brokers who execute the orders of the clients when clients raise a request for buy or sell online.
3. Depository:
A depository is an institution or a Custodian that holds the shares or securities of the traders in a Dematerialized form (Electronic form). These depositories hold securities of the investors in its own name though the beneficial owners are the traders or investors.
There are mainly 2 depositories in India namely
- Central Depository Services India Limited (CSDL)
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
The main function of the depository is to mitigate the risk of fake transfers or theft of Physical shares certificates by converting the entire process into dematerialized form.
4. Clearing House:
A clearing house is an entity charged with the function to ensure the financial integrity of trade. These are established to look after the settlement of the trade. It minimizes the credit risks by being a counter party in all trades and guarantees the settlement of trade in the event of default of trading participant as it collects the margins on each transaction depending upon the price movements. Every transaction between the buyer and the seller is substituted by two contracts so that the clearing house becomes the counterparty to each trader that is becomes buyer for each seller and a seller for each buyer. It ensures the delivery of payment for the assets on the maturity date for all outstanding contracts.
Margins are of three types,
Initial margin: It refers to funds paid as guarantee to ensure that the party will perform his obligation under the contract.
Maintenance Margin: It refers to the value over and above the initial margin. This maintenance margin has to be maintained in a margin account at all times after the initial margin requirement.
Variation Margin: It refers to funds that are required to be deposited in, or paid out of a margin account that reflects the changes in the value of the relevant instrument.
The Federal Reserve board sets the rules for margin requirements. Though the Federal Reserve board sets margin requirement at 50%, the brokerage firms may set a higher margin requirement for minimizing its risk.

5. Stock exchange:
A stock exchange is a market place enabling the traders to trade their securities.
A company that wants to issue its securities to the public has to list itself in with the stock exchange. Once listed, the securities of the company can be bought and sold by investors.
For more information about Stock exchange, visit: Capital Markets Of India
6. Settlement Process and Cycle:
Settlement period refers to the time between the date of transaction and settlement. SEBI introduced a new settlement cycle called "Rolling settlement". This cycle starts from the day the transaction is made and ends on the day the settlement is done. Settlement period refers to the period where the buyer has to pay for the trade and the seller has to deliver his securities to the buyer.
With effect from 1st April 2003, securities in the Equity segment and fixed income securities that are listed on BSE, the settlement has to be made by “T+2” days where ‘T’ refers to the Transaction date and the settlement is done on the 2nd day from the transaction date. The settlement is done on the 2nd business day excluding Saturdays, Sundays and Exchange trading holidays.
The following picture helps in better understanding of the rolling cycle.
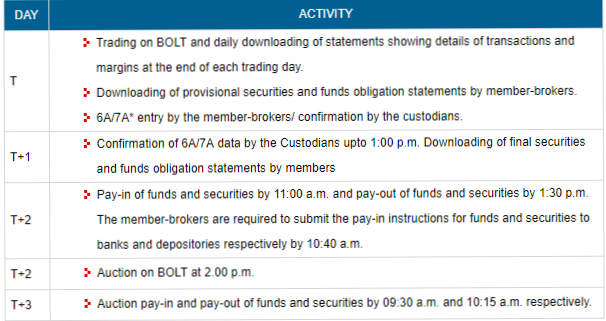
Image Source: BSEindia
Rolling settlement helps in better and quicker payments. This helps the investors increase their liquidity. For an Investor, this rolling settlement reduces delays and also reduces the tendency for price trends to get exaggerated.
The BSE provides an efficient and transparent market for trading in debt instruments, equity and derivatives. This is performed through a system known as BOLT - BSE's Online Trading System.
Article Comments
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.