ERP CRM Securities To Be Concerned About Before Selecting Best ERP CRM Software

Back in July 2018, the US DHS (Department of Homeland Security) issued an alert warning to raise a sign of alarm with regard to securing ERP CRM systems before it gets too late for the companies to act. Attacks on ERP CRM systems have been quite frequent these days and can easily make the organization end up losing millions of dollars as well as significant number of customers. As it is a well-known fact that ERP implementation is a tough nut to crack, likewise ERP CRM Security is a topic that should not be taken lightly. There are several failed cases of ERP Security and CRM Security, which lead to shareholders’ lawsuits and financial meltdowns.
Thus, the importance of understanding these security factors is inevitable in order to lead a successful ERP security and CRM security implementation. And to help you with the same we have crafted this article for discussing about the ERP CRM securities to be concerned about before selecting the best ERP CRM software.
What is ERP security and why it is being over-emphasized?
ERP and CRM systems are undoubtedly some of the important company assets. Not only the said systems handle the day-to-day company tasks, but these also store a humongous amount of data including both external and internal resources. Most important kinds of company data may include customer data, contract data, production plans, financial data, or even trade secrets, losing which means losing millions of dollars and customer trust at the same time. No company will even entertain the prospect of the same, and this is exactly why ERP CRM security is being over-emphasized as days go by.

Now to answer what ERP security is, it can be stated that it is the practice of involving effective security measures aimed at guarding the entire Enterprise Resource Planning systems against illegitimate and unauthorized access to maintain the integrity of the ERP systems. The same goes with CRM security as well. Securing a CRM system revolves more around securing confidential and crucial customer data. With impending security threats, ERP and CRM businesses have started to invest in robust measures to protect their systems against cyber bullies and their exorbitant ransom.
Considering the digital transformation, the most valuable resource in the current world scenario is no longer crude oil or petroleum, but Data. Information! Not at all exaggerated but a real fact! Hackers tend to target the more vulnerable and easier sources which are the smaller businesses since they rarely have strong and sufficient cybersecurity, whereas global enterprises with sturdy and well-built cybersecurity protections ironically tend to attract fewer cyberattacks. The worst part, small businesses often end up with data breaches, coping with financial disintegration, and are overwhelmed by the lost business.
Unfortunately, all the critical data and business information in one place are prone to risks of external threats, just like having all of your eggs in one basket. This implies that you are more vulnerable as an organization. Thus, ERP security and CRM security are indispensable countermeasures to ensure the safety of the exposed and sensitive data of your organization.
Elements of ERP CRM Security:
To keep your ERP CRM systems secure and confidential information unscathed, ERP CRM Security covers different areas such as:
1. Infrastructure Security
It refers to the measure of providing protection and security to the critical systems and assets that includes both hardware and software such as end-user devices, data center resources, cloud systems and networking systems against cyberattacks, disruptions, malpractices or security threats. It aims to develop high-level tactical security plans in order to protect the entirety of the organization’s technological perimeter. Top concerns include resilience, boost security measures, downtime, customer attrition, brand and reputation abrasion, and compliance costs.
2. Network Security

The policies and practices adopted by the organization to prevent, detect and control unauthorized access, mishandling, or modification of a computer network and network-approachable resources. The main focus is to safeguard access to files and related directories in a computer network against misuse, cyber threats, hacking, and intrusions. Measures that can be espoused to ensure Network Security Protection:
- Firewalls, especially Next Generation Firewalls that give attention to blocking malware and application-layer attacks.
- Network Segmentation where the potential intimidations outside the network are banned ensuring that the organization’s hypersensitive data awaits in the premises itself.
- Defining Access Control is equally essential just like the rest of the measures. The application of this action will thereby, deny the unsanctioned access and threats. Policies like Role Based Access Control (RBAC) and Identity and Access Management (IAM) will help you to identify that both person and device are authorized to access the asset.
- Strongly adopting the Zero-Trust Security approach to avoid complexities and risks with a state of mind that no user, no device, no workload or system should by any chance be trusted by default. Know more about Zero-Trust.
- The transformation from On-premises to Cloud ERP and embracing remote workforce have emerged with an idea of a more user-centric network rather traditional network we once knew. The increasing adoption of Remote Access VPN (like Perimeter 81) has helped businesses establish a secure connection between their network and devices used by remote employees. It creates a certain kind of virtual tunnel between an employee’s device and company’s network. This simulated tunnel enters the public internet, but the data sent from pillar to post is protected by encryption and security protocols to keep it private and locked.
- Sandboxing is another security mechanism for running code in an isolated test environment on a network to run programs or open files without hampering the application, platform, or system. It is actually an effective way to defend against Zero-Day Threats/ Zero-hour Threats, which makes it one of the most plausible measures for ERP CRM security.
- Migration from On-premise to Cloud infrastructure implies that now more and more sensitive data and information are stored in the clouds and that has to be protected against malicious actors. Defining a security baseline before the organization starts using cloud network is very crucial to avoid common security pitfalls in the cloud environment.
3. Operating System Security
A security practice of ensuring operating system safety from threats and attacks, enabling different applications and programs to perform required responsibilities and avoid unauthorized interference. There are various approaches in adherence to the following:
- Conducting regular OS patch updates
- Installation of antivirus engines and software
- Scrutinizing incoming and outgoing network traffic through a firewall
- Setting up secure accounts with required privileges only such as User management
4. Database Security

It comprises of various tools, measures, processes and methodologies that establish security inside a database environment to guard it against malicious cyberattacks, illegitimate use, and data breaches. Some of the known database security cyber threats are:
- Insider Threats- An insider threat can be a security risk from within the targeted organization, it can be a malicious insider with an ill-intent, a negligent person who exposes the database to attack through unsympathetic and inconsiderate actions or an outsider who deceives credentials through social engineering.
- SQL/No SQL Injection (SQLi) Attacks- It is the most common web hacking technique that might destroy your database. It is the placement of malicious code in SQL statements via web page input. By doing this, the attackers can authorize the web page or application and can go around retrieving the content of the entire SQL database. You can prevent it by input validation and parametrized queries including prepared statements. The coder must eliminate potential malicious code elements such as single quotes, and best idea would be to turn off the visibility of database errors on production sites.
- Buffer Overflow Attacks- A buffer overflow or say, buffer overrun is a software coding mistake and occurs when there are loads of data in a buffer that it can actually handle, which causes data to overflow into adjacent storage. This vulnerability can ultimately lead to a system crash or cyberattack. C/C++ applications are the easy targets of buffer overflow attacks, therefore, to prevent the same, developers of C and C++ programming languages should eschew standard library functions that are not bounds-checked. Include consistent testing to detect and fix buffer overflows and enforce bounds-checking at run-time to ensure that data is within acceptable boundaries.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks- It is a type of cyber-attack where a malicious actor aims to interrupt the device’s normal functioning by overwhelming or flooding a targeted device with requests until normal traffic is unable to be processed which subsequently results in denial-of-service to additional requests.
ERP CRM security facts to check before opting for an ERP CRM software
ERP has evolved significantly over the years and being a fully comprehensive system that covers such a broad spectrum, naturally, there are going to be a few chinks in the armor and vulnerabilities that are to be looked after. Below are some of the common ERP security and CRM security facts which you should check before selecting the best ERP: -
1. Updates Behind Schedule: ERP systems support many of the organization’s core business processes and operations and if it lags behind, it will hinder your business efficiency and decision-making capabilities. And if you are using an outdated ERP and the updates are behind schedule, then it will not only impede your business growth and hold you back from staying competitive, but you will also find yourself on the verge of security risks such as vulnerability to hacking, vandalism, or viruses.
Reports say that a whopping 87% of businesses use archaic software, including ERP CRM software which are not up to date. Updates happen for a reason, occasionally to introduce new features but most importantly to address Achilles' heel. The world of cybercrime is hyperactive, and hackers are constantly discovering ways to attack software.
Thus, your prime focus should be on timely ERP updates including all the ERP CRM security patches and ask for more questions to your vendor regarding the automatic updater which will apply software updates when available.
2. Full Access Rights: Undoubtedly, the external sources possess the greatest business security threats, but does that imply that we should become reluctant and sit back and neglect in-house risks? Full Access rights should not be provided by default, because it is very necessary to keep an eye on who has access to what data. It is worth noting which employees have permission to make alterations to the system. Let us understand it with an example- In most cases, a software developer’s job is to develop software, design, build and maintain computer programs, they would not require a sneak peek into an employee’s salary information. Access Rights largely depend on the needs and requirements of the business but generally, it should depend on a “need-to-know” basis. There are 3 main types of access control systems namely:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC)- Whether you know it or not, you are certainly using DAC in your day-to-day computing life. Under DAC, the owner of the object is usually the person who designed it. This runs on the philosophy that every object has an owner and the owner are allowed to allocate access at their discretion.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)- Commonly used by the government and thus considered the stringent level of access control systems.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)- Also known as non-discretionary access control, used when rights are assigned based on organizational roles instead of individual user accounts. Runs on the “least privilege” principle, permitting access required to do their job since access is linked to their job.
3. Inadequate Training: User training is often deemed as an "Underdog" in an ERP CRM implementation process. In some cases, risks may be malevolent and on purpose but most of the time, it is likely to occur due to the lack of proper understanding and knowledge and inadequate user training. Most of the attention is allotted to implement the system precisely, but enterprise undermines the ERP CRM training to employees and lays a very little emphasis on the same. If done correctly, it can ensure immeasurable success to the company. Ultimately, it’s the employees of the company who are the end-users and they must learn how to operate the system, for which they should be given proper and systematic training to use ERP CRM to its full potential. The errors caused by them due to the lack of understanding may be categorized as “innocent mistakes”, but you cannot leave your business exposed to security threats. You must ask your ERP provider whether system training is included as standard and well-equipped staff to train new hires and make sure certain business protocols are readily available and accessible to the employees.
4. No Automatic Trust: Migration from On-Premises to Cloud ERP systems is gaining humongous popularity. Although there are many advantages attached to it such as freeing IT department for more profit-oriented tasks, and they can save you more money. But a slight downside to it is that you have to place your entire ERP security and CRM security in the hands of a third-party provider. Thus, you are required to consider cloud provider very prudently and without being afraid of asking questions, asking around , and reading reviews. You must pay utmost attention to their security processes and data compliance rules and regulations.
5. Two-factor Authentication: Password cracking is one of the most easiest and common forms of hacking, so it doesn’t actually add up to protect the sensitive and confidential business data just with a simple password (one-way authentication) which can be interpreted by hacking experts with no trouble. Therefore, two-way authentication stands out as clear solution.
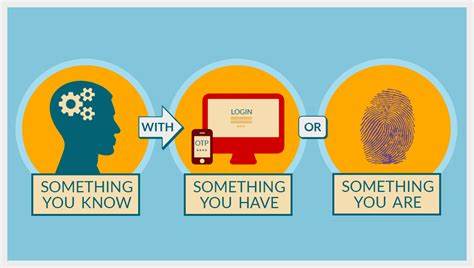
Two-factor authentication is a mighty security tool to safeguard data and users from the increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. It lets you not rely on passwords alone but it provides a two-way authentication process that helps in adding another layer of security to your business. The cybercriminals find it quite difficult to steal user’s identities and access their device and systems. It also helps the organization to keep attackers at bay even if a user’s password is stolen or hacked.
6. Identifying Configuration Vulnerabilities: One of the prime influences in many data breaches is configuration vulnerabilities. Almost all cloud providers offers a wide variety of controls for your business environment. Now you have to spare time to assess these controls and identify which one will provide significant security benefits. Guidelines such as the CIS (Center for Internet Security) benchmark can render great help when it comes to learning about industry best practices for securing IT systems, software and networks. Hunting down vulnerabilities and identifying what measures should be in place to effectively curtail risks is essential for securing the underlying cloud infrastructure. Like this, you can keep a check on the ERP security means and CRM security means before selecting the best ERP and CRM system.
Conclusion:
In an organization, the top management is aimed towards what’s best for the business. Everyone should learn together and respect each other’s viewpoint. ERP security and CRM security should not be considered burdens instead, paint them a picture to show what good can occur if the measures for the same are carried out in a better way, how you can actually make your business even more secure and provide your employees and clients with better and enhanced experience.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.