Integration Of Blockchain And ERP: A Great Futuristic Solution Beyond Cryptocurrency!

Often, most people associate blockchain tech with cryptocurrency or bitcoin, but the former term is much more than just Bitcoin or Cryptocurrency. They might be related but these two concepts are quite different.
Supply Chain in today’s scenario is complex, multi-echelon, highly disjointed, and geographically spread across corners of the world. All these together alongwith different government policies and human behavior make it nearly impossible to investigate incidents and events in case of supply chain disruptions. The inherent cost involved in managing supply chain intermediaries, their consistency, reliability, traceability, and transparency further set hurdles in the supply chain. The solution to such complicated issues lies in improving supply chain transparency through the concept of Blockchain.
This article helps you to understand what blockchain technology is, and how it is changing the face of the supply chain and delivering transparency and authenticity. The article first discusses and introduces the concept of blockchain technology, the protocols of blockchain, and its architecture. After deep dive into the design of blockchain, we will talk about the challenges of blockchain in the supply chain domain and lastly, the synergy and integration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems of the supply chain domain with blockchain.

Introduction to Blockchain Technology:
The advent of Cloud ERPs has enabled supply chain processes to be more global with the ability to source and manufacture with the best economy, have greater than before quality, be closest to the market, and impart augmented value to the customer. However, it has ended up being more complex and rigid. The transactions include inefficiencies, frauds and pilferages, and a greater trust deficit, which gave rise to numerous codes like the United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC), Universal Product Code (UPC), compliance with Country of Origin (COO), and Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS). All these help the supply chain to be more reliable but escalate its cost. The need of the hour is visibility in the supply chain, but it is next to impossible with the existing architecture.
As of today, we cannot map, link, trace, or make the entire supply chain of a particular product visible from cradle to grave, but there are new developments in technology and communication architecture that can make these possible and achievable. And the answer to this problem lies in the technology of blockchain. A definition filled with jargon and difficult words won’t help. A simple explanation of the term is a distributed ledger, which is a list of transactions, that are being shared among a number of computers rather than being stockpiled on a central server. The transaction logged in it will have supply chain-related information like location, price, date, and quantity which will be present in the distributed ledger. The publicly available information in the distributed ledger makes it possible to trace back each and every transaction to the grassroots. It becomes almost impossible for a single party to manipulate as they do not hold the ownership. In fact, blockchain is considered “Unhackable”, as it is a groundbreaking solution in many ways-
- World’s first distributed consensus system
- World’s largest and leading P2P (peer-to-peer) network
- World’s first and largest write-only-public ledger
- The only ledger that tends to become more secure with increasing volume and time.
Protocols of Blockchain Technology:
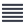
Every time a transaction occurs between the members of the bitcoin network (which is a decentralized network), it needs to be verified and validated to ensure that every transaction occurring within the network is between two individual accounts and there lies absolutely no risk of double spending. Now, who does the verification? The verification of transactions is carried out by members of the blockchain network known as “miners”. These miners use their expertise, software, their own coding skills, and computers to verify the transactions. The “block” in Blockchain refers to the occurrence of transactions. The verification of the transaction or block, the availability of the validated transaction thereafter, and its irreversibility paves the platform for the blockchain. After the substantiation by the fastest miner, the birth of a legitimate and immutable block takes place. The transactions are consolidated in a block and each block is associated with the previous transaction block via addresses. Clustering all these blocks leads to the formation of blockchains. The grouping of blocks occurs as per the protocol that is dictated by the algorithm and this protocol is referred to as the Blockchain Protocol. The figure below illustrates the Blockchain Protocol-
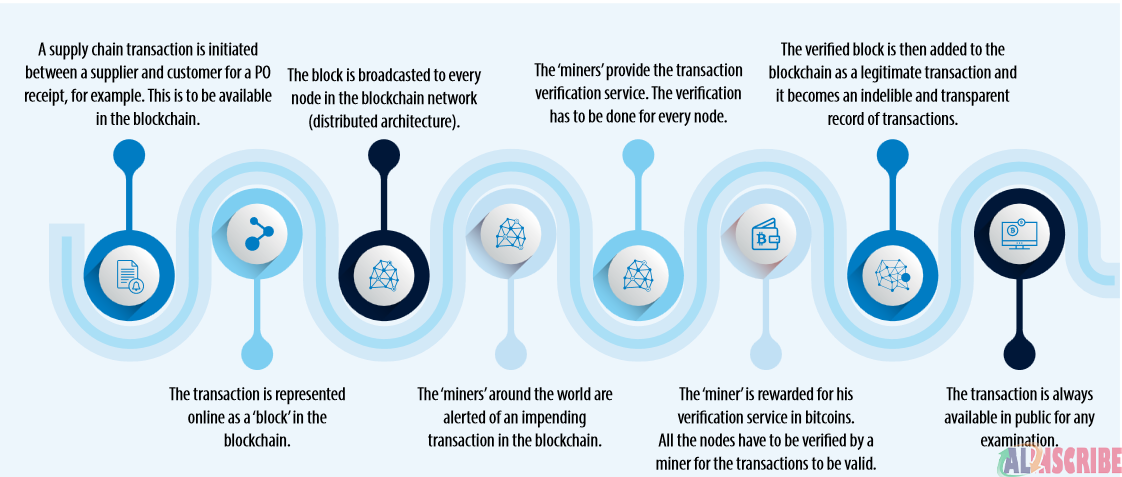
Architecture of Blockchain Technology:
The blockchain operations are segregated into three layers, each layer having its own significance, specific purpose, and role. The Blockchain layer, Data Store layer, and Application layer define the architecture of the Blockchain.
1. Blockchain layer:
It maintains the “pointers” or “hashes” of transactions. Helps to represent the notifications to a status change and validate the data integrity. The blockchain layer helps you to connect with the Data Store layer. It ensures transparency through decentralization, data integrity, and immutability.
2. Data Store/Collect layer:
The blockchain layer just refers to the hashes or addresses while the Data Store layer or the Collection layer actually stores the data. This layer is arranged through auto-hash transactions onto the public chain at required intervals. The data is encrypted, therefore, if a third party wishes to derive any meaningful information from the data, they cannot unless they have specific keys that allow them to decrypt each individual record. This particular layer throws light on permission, scalability, and security.
3. Application layer:
This layer processes and interacts with the other two layers and transforms them into a useful business application. The application layer has monitoring units that pinpoint changes in the blockchain layer, read the pointers, extract the decrypted data from the Data Store layer and final validation is performed. This layer also has the capability to interact with ERP applications like Oracle, SAP. Infor etc.
Challenges for Blockchain:
Some of the major limitations are as below:
1. Regulatory and Legal Acceptance:
Blockchain lacks a legal framework. Single ownership or autonomy is missing, thus a legal framework on territoriality for issues like jurisdiction and the applicable directives and principles needs to be there. Its a critical requirement as each network node may be in a different geographical location under legal law or enforcement like chalk and cheese.
2. Central Administrator:
Again, there is no central administrator or supervisory authority for the distributed ledger. Eventually, this leads to a concern that there is no person, group of people, or organization responsible for the functioning of distributed ledgers and the crucial data contained in them.
3. Validity of Stored Information:
It is very essential to have a legal deed declaration of ownership of the existence of an asset on the node or genuine and legitimate proof of the subsistence of the said asset.
4. Standardized Communication:
To facilitate interoperability between blockchains, standards are required that can be in XML (eXtensible Markup Language), or EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) formats which are accepted forms of communication.
5. Beyond the Hype-financial transactions:
Often it is deemed that most of the blockchains are financial-transaction validation-oriented, but they are not utilized to their full potential. They need to diversify in other fields like manufacturing, procurement, logistics and HR. The growth will certainly be phenomenal after that.
6. High Energy Consumption:
In the case of Blockchain, energy consumption remains one of the biggest issues with miners. Researchers at Cambridge University have estimated that Bitcoin consumes more energy than the entire nation of Switzerland. The energy is primarily supplied to keep the complete network alive and working all the time. That’s the case of just one blockchain, imagine the condition if we have many more such networks.
7. Latency:
Blockchains suffer from high latency issue as there is a time lag between the verified blocks and their addition to the ledger. For some of the leading blockchains, the time lag varies between around 17 seconds and a minute which is considered way more than the average database transaction time.
Transactions recorded among the blockchain network is surely a challenge but also the need of the hour. There are a few independent software vendors who are developing individual connectors of some ERP or transactional systems with these blockchains. With greater connection and more popularity, blockchain technology can be easily integrated with ERP applications.
Blockchain ERP Integration: Benefits!
As blockchain continues to mature, it has witnessed its promising future in the tech industry quickly. IT experts and professionals understand how it can influence our daily life, so it becomes necessary to integrate it with various business application systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), etc. So, let us check how Blockchain integration with ERP enhances the existing features of the latter:-
1. Eliminates trust gap and extends trust boundary:
ERP systems tend to create visibility problems between different departments known as trust gaps. Blockchain ERP integration eliminates these trust gaps between siloed ERPs while providing visibility and transparency throughout the system.
2. Transparency in the Supply Chain:
Blockchain and ERP integration help to improve the automation supply chains by reducing the visibility problems within the supply chains. The decentralization attribute of Blockchain gives companies the potential to unify a large supply chain network. Each member can trace the product journey from manufacturing to the final delivery. Each transaction would be recorded on the blockchain automatically. Companies will have full visibility into the entire supply chain, however, if they want, they can still record and keep the private data relevant.
3. Ability to verify and authenticate identities:
ERP systems, for a long time, have been used for recording financial transactions like process claiming of insurance and financial institutions. For this, companies are required to scrutinize the customer’s identities and authenticate financial transactions. It can also be used to verify customers’ identities as a part of post-sales support or during the servicing of older products, provided they are under warranty.
4. Risk-free Payment:
Blockchain is reckoned for its robust security features, particularly in financial transactions. It ensures risk-free transactions, henceforth, banks and insurance companies are expected to use blockchain-based authentication systems. Blockchain ERP integration ensures that B2B purchases and payments meet regulatory compliance.
Integration with ERP, WMS, and MES systems will diminish disputes over invoices, shipments, returns, and purchases.
With Customer Relationship Management software, it can bring transparency around customers and the chain of ownership.
The benefits of Blockchain ERP integration are twofold. Firstly, it will ensure transparency, and secondly, it will significantly reduce the cost of tracking and reporting, considering multi-echelon and multi-staged supply chains.
Use cases:
- Finlync’s distributed ledger is considered the world’s largest blockchain-agnostic integrator for ERP systems. Finlync has developed a seamless plus-and-play integration for SAP, Ethereum, and Hyperledger blockchains.
- Skye, a Norway-based company has many versatile products to offer. It has developed integrations of SAP with other blockchains that offer integration services in finance, HR, and supply chain management.
- The advent of middleware technologies that can connect ERP systems with different blockchain networks. Let us take the example of Microsoft’s Project Bletchley. It is an open-source framework that allows blockchain ERP integration. Its focus is on security and governance requirements and thus, includes features such as a gateway or identity, key and crypto services so that non-blockchain clients are able to communicate within the network.
- There are several use cases related to procurement and logistics areas of supply chain which can leverage blockchain technology. In a survey conducted by IBM, results say that there are more than 100 million dollars of invoices worldwide that are in dispute between buyer and supplier, and which takes on an average of 44 days to settle. Using Blockchain ERP integration, it can easily be avoided up to approximately 90-95%.
- Another powerful use case of blockchain ERP integration can be the replacement of EDI. Currently, EDI messages are transferred using blockchain nodes with confidential data stored/accessed through the private key. Contracts, agreements, certificates, or other documents attached to sales and purchase orders can be removed from the transactional system and can be made available in blockchain, which will be attached to the transactions, ensuring complete transparency and ownership.
Conclusion:
It can be concluded that a lot of research has already been done on Blockchain with ERP applications, and the field still remains wide open. Blockchain works as an additive technology for ERP just like AI, IoT, and other future trends. There are yet plenty of efforts underway to establish Blockchain’s capabilities. So, if not now, wait for the near future, once the technology matures, its adoption will increase at a commendable rate.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.